 Cannabis sativa is an annual herbaceous flowering plant native to Eastern Asia, now globally distributed due to extensive cultivation. It has been grown throughout history for various purposes including industrial fiber, seed oil, food, recreation, religious and spiritual activities, and medicinal uses. The plant was first classified by Carl Linnaeus in 1753.
Cannabis sativa is an annual herbaceous flowering plant native to Eastern Asia, now globally distributed due to extensive cultivation. It has been grown throughout history for various purposes including industrial fiber, seed oil, food, recreation, religious and spiritual activities, and medicinal uses. The plant was first classified by Carl Linnaeus in 1753.
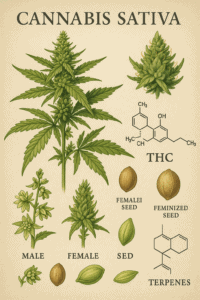
Cannabis sativa flowers are unisexual, with male and female plants typically exhibiting different physical characteristics. Females produce seeds in racemes, and males disperse pollen then die before seed maturation. Environmental factors like light cycles can influence the sexual expression of the plants, although they generally produce equal numbers of male and female plants under a 12 to 14-hour light period. Additionally, monoecious plants (both male and female parts) can occur naturally or be induced artificially. Commercially, “feminized” seeds are often sold, derived from genetically modified female plants.
The primary psychoactive component of Cannabis sativa is Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), though the plant contains over 500 compounds including more than 113 cannabinoids like CBD, which counteracts some of THC’s effects. The chemical profile varies significantly among different strains, influencing the plant’s effects on users. For example, sativa strains are known for their cerebral high, while indica strains are sought for their sedative effects.
Cannabis sativa is also notable for its terpenes, which contribute to its aroma and are believed to interact synergistically with cannabinoids to enhance the plant’s effects, a phenomenon known as the “entourage effect.”
Cultivation requirements for cannabis include specific light cycles for flowering, optimal pH levels for growth, and methods like parthenocarpy in females to enhance resin production. While traditionally propagated by seeds, tissue culture methods are also used, especially for medicinal clones. Sativa plants favor warm climates and have a longer flowering period compared to indica strains.
Overall, Cannabis sativa remains a complex plant with diverse applications and ongoing interest in its pharmacological and therapeutic properties.